Set up Snowflake
This guide walks through configuring Snowflake to work with Atlan's data quality studio by creating the required roles, setting up database objects, and granting the necessary privileges.
Some capabilities shown here may require additional enablement or licensing. Contact your Atlan representative for details.
System requirements
Before setting up the integration, make sure you meet the following requirements:
- Snowflake Enterprise or Business Critical edition
- Dedicated Snowflake warehouse for running DQ-related queries
Before you begin
Data Quality Studio is a paid feature that requires access. You can request access by following the steps below so the team can enable it for you, while you continue setting up Snowflake.
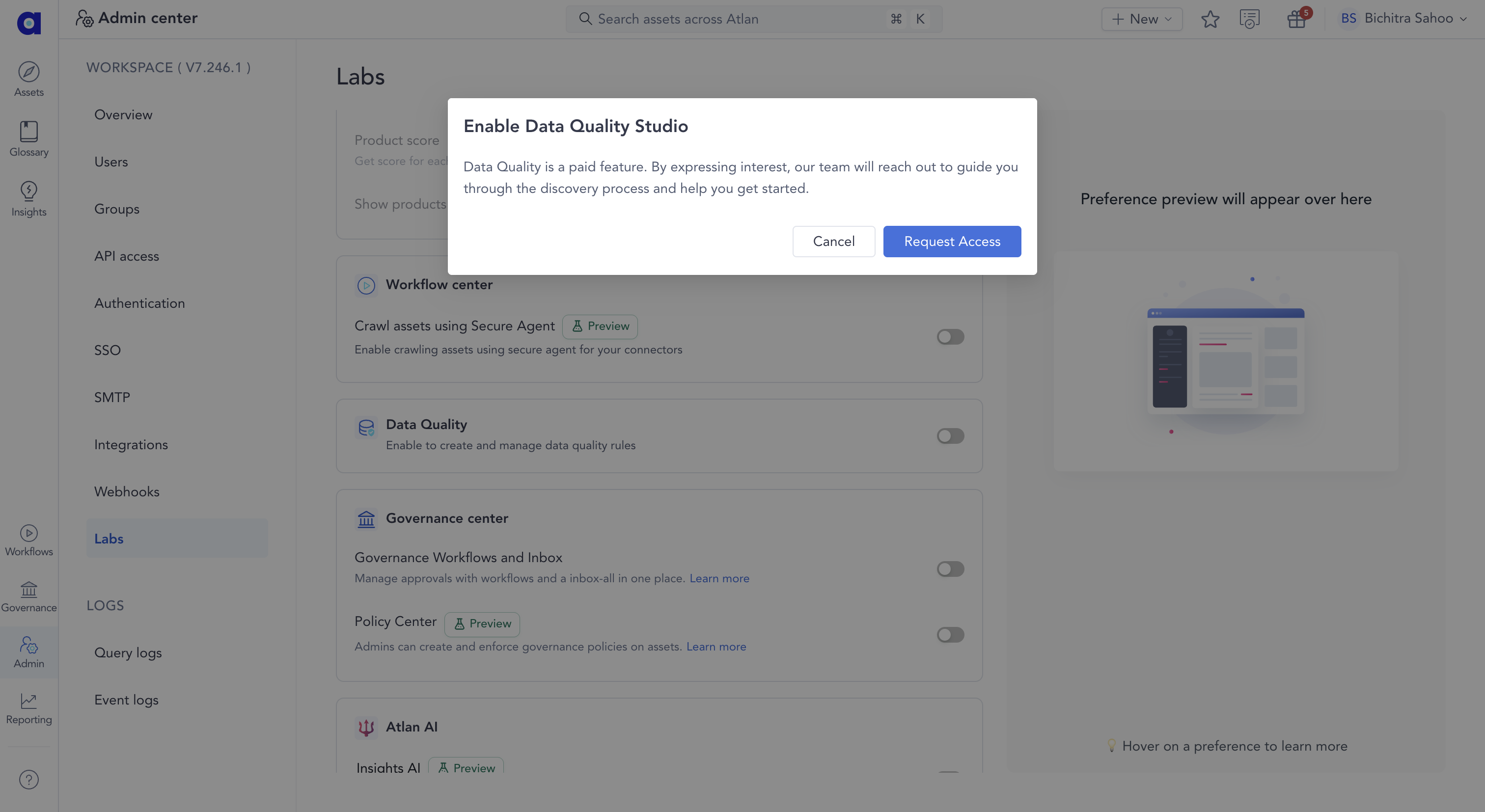
- Navigate to Admin > Labs in Atlan
- Turn on the Data Quality toggle
- Click Request Access when the popup appears
After you request access, the Atlan team reviews and grants access, after which you can proceed to enable Data Quality for Snowflake.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, complete the following steps:
- Obtain
ACCOUNTADMINrole or equivalent administrative privileges in Snowflake - Identify your dedicated warehouse name for DQ operations
- Have access to create a new Snowflake user for Atlan
- Review Data Quality permissions to understand required privileges
Set variables
Set the following variables to configure your data quality environment. If you want to enable data quality for multiple Atlan connections on the same Snowflake account, rerun this setup with different values for the variables. A dedicated database is required for each Atlan connection.
-
Set primary variables with your environment-specific values:
-- Replace with your Atlan user name
SET ATLAN_USER_NAME = '<atlan_user_name>';
-- Database for DQ objects (customize if needed)
SET ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE = 'ATLAN_DQ';
-- Replace with your DQ warehouse name
SET ATLAN_DQ_WAREHOUSE = '<warehouse-name>';
-- Admin role for setup (not granted to Atlan user)
SET DQ_ADMIN_ROLE = 'DQ_ADMIN';
-- Service role for Atlan operations
SET ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE = 'ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE'; -
Set the derived variables that generate the required schema and procedure identifiers without modifying their default values.
-- Do not modify the variables below:
SET _SHARED_SCHEMA = (SELECT $ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE || '.SHARED');
SET _DMFS_SCHEMA = (SELECT $ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE || '.DMFS');
SET _MANAGE_DMF_PROCEDURE = (SELECT $ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE || '.SHARED.MANAGE_DMF');
Create roles
Create two roles for the integration:
-- Create DQ Admin Role
CREATE ROLE IF NOT EXISTS IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT OPERATE, USAGE ON WAREHOUSE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_WAREHOUSE) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
-- Create Atlan Service Role
CREATE ROLE IF NOT EXISTS IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT OPERATE, USAGE ON WAREHOUSE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_WAREHOUSE) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
Create user
Create a dedicated Snowflake user for Atlan following your organization's standards, then grant the service role:
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_USER_NAME);
GRANT ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE) TO USER IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_USER_NAME);
Set up database objects
Create the database, schemas, and stored procedure required for Atlan data quality operations.
-
Create the required database structure:
-- Create database (customizable via ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE)
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE);
-- Create schemas
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS IDENTIFIER($_SHARED_SCHEMA);
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS IDENTIFIER($_DMFS_SCHEMA);The database set in
ATLAN_DQ_DATABASEserves as a container for all objects related to Atlan Data Quality. TheSHAREDschema provides a separate namespace for shared procedures and functions, while theDMFSschema is required for custom Data Metric Functions (DMFs). -
Create stored procedure for DMF management:
View procedure code
/**
* Manages Data Metric Functions (DMF) operations for Snowflake tabular entities.
* This procedure handles various DMF operations including:
* - Creating and managing DMFs (CREATE_DMF)
* - Attaching/detaching/suspending/resuming DMFs on entities (ATTACH_DMF, ATTACH_DMF_WITH_ROLE, DETACH_DMF, SUSPEND_DMF, RESUME_DMF)
* - Managing DMF schedules (UPDATE_SCHEDULE)
* - Executing read-only SQL expressions (EXECUTE_SQL)
*
* The procedure runs with the privileges of the procedure owner and includes comprehensive
* validation of all inputs and permissions before executing any operations.
*
* @param {string} ACTION - Operation to perform (GET_PROCEDURE_VERSION, ATTACH_DMF, ATTACH_DMF_WITH_ROLE, DETACH_DMF, SUSPEND_DMF, RESUME_DMF, UPDATE_SCHEDULE, CREATE_DMF, EXECUTE_SQL)
* @param {string} ENTITY_TYPE - Type of entity (TABLE, VIEW, MATERIALIZED VIEW, EXTERNAL TABLE, ICEBERG TABLE)
* @param {string} ENTITY_NAME - Fully qualified name of the entity (database.schema.name)
* @param {string} [DMF_NAME=null] - Fully qualified name of the DMF (database.schema.name)
* @param {string} [DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON='[]'] - JSON string containing column configurations
* @param {string} [SCHEDULE_TYPE=null] - Schedule type (MINUTES, CRON, ON_DATA_CHANGE, NOT_SCHEDULED)
* @param {string} [SCHEDULE_VALUE=null] - Schedule value based on type
* @param {string} [DMF_DEFINITION=null] - Read-only SQL expression defining the DMF or used by EXECUTE_SQL
* @returns {string} - JSON string with operation status and result message
*/
CREATE OR REPLACE SECURE PROCEDURE IDENTIFIER($_MANAGE_DMF_PROCEDURE)(
ACTION STRING,
ENTITY_TYPE STRING DEFAULT NULL,
ENTITY_NAME STRING DEFAULT NULL,
DMF_NAME STRING DEFAULT NULL,
DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON STRING DEFAULT '[]',
SCHEDULE_TYPE STRING DEFAULT NULL,
SCHEDULE_VALUE STRING DEFAULT NULL,
DMF_DEFINITION STRING DEFAULT NULL
)
RETURNS STRING
LANGUAGE JAVASCRIPT
EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS
$$
const PROCEDURE_VERSION = "1.0.0";
// -----------------------------------------------------UTILITY FUNCTIONS-----------------------------------------------------
/**
* Executes a SQL query with parameters
* @param {string} sqlText - SQL statement to execute
* @param {Array} [binds=[]] - Array of bind parameters for the query
* @param {boolean} [returnFirstRow=false] - Whether to return only the first row
* @returns {Object} Object containing execution result or error information
*/
function executeQuery(sqlText, binds = [], returnFirstRow = false) {
try {
if (!sqlText)
return {
isErrored: true,
message: "SQL Text is required",
result: null,
};
const statement = snowflake.createStatement({ sqlText, binds });
const result = statement.execute();
const response = {
isErrored: false,
message: "",
result: null,
};
if (returnFirstRow) {
response.result = result.next() ? result : null;
return response;
}
response.result = result;
return response;
} catch (err) {
return {
isErrored: true,
message: `${err.code} - ${
err.message
} - ${sqlText} with binds: ${binds.join(", ")}`,
result: null,
};
}
}
/**
* Safely parses a JSON string
* @param {string} jsonString - JSON string to parse
* @returns {Object} Parsed JSON object or null if invalid
*/
function safelyParseJSON(jsonString) {
try {
return JSON.parse(jsonString);
} catch (err) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Validates a number within a range
* @param {string} value - Number to validate
* @param {number} min - Minimum value
* @param {number} max - Maximum value
* @returns {boolean} True if number is valid
* @returns {boolean} False if number is invalid
*/
function isNumberValid(value, min, max) {
const num = parseInt(value, 10);
return !isNaN(num) && num >= min && num <= max;
}
/**
* Escapes and quotes a Snowflake identifier
* @param {string} identifier - Raw identifier to normalize
* @returns {string} Properly quoted identifier safe for SQL
*/
function normalizeIdentifier(identifier) {
return `"${identifier.replace(/"/g, '""')}"`;
}
/**
* Returns the database currently in use for this procedure execution
* @returns {string} Database name
* @throws {Error} If database cannot be determined
*/
function getCurrentDatabaseName() {
const res = executeQuery("SELECT CURRENT_DATABASE() AS DB", [], true);
if (res.isErrored || !res.result) {
throw new Error("Failed to determine current database");
}
const db = res.result.getColumnValue(1);
if (!db) {
throw new Error("Could not fetch current database name");
}
return db;
}
function getDatabaseOwnerRole(database) {
const res = executeQuery(`SHOW DATABASES LIKE '${database}'`, [], true);
if (res.isErrored) {
throw new Error("Could not fetch database owner role");
}
const role = res.result.getColumnValue('owner');
if (!role) {
throw new Error("Could not fetch current database owner role");
}
return role;
}
/**
* Retrieves all columns for a given entity. Validates that the entity exists and procedure owner has access to it.
* @param {string} entityName - Fully qualified entity name
* @returns {Array} Array of column objects with name and dataType properties
* @throws {Error} If entity doesn't exist or is inaccessible
*/
function getAllColumnsForEntity(entityName) {
const sqlText = "SHOW COLUMNS IN IDENTIFIER(?)";
const binds = [entityName];
const { result, isErrored, message } = executeQuery(sqlText, binds);
if (isErrored) {
// Validates that the entity exists and procedure owner has access to it
throw new Error(message);
}
const columns = [];
while (result.next()) {
const column = {
name: result.getColumnValue("column_name"),
dataType: JSON.parse(result.getColumnValue("data_type")).type,
};
if (column.dataType === "FIXED") column.dataType = "NUMBER";
columns.push(column);
}
return columns;
}
/**
* Validates that the DMF is valid and exists
* @param {string} dmfName - Fully qualified name of the DMF
* @param {string} dmfArguments - Arguments for the DMF
* @returns {boolean} Whether the DMF is valid
* @throws {Error} If DMF is invalid
*/
function isDMFValid(dmfName, dmfArguments) {
const { isErrored, message } = executeQuery(
`DESCRIBE FUNCTION IDENTIFIER(?)(${dmfArguments})`,
[dmfName],
true
);
if (isErrored) throw new Error(message);
return true;
}
/**
* Checks if a timezone is valid
* @param {string} timezone - Timezone to validate
* @returns {boolean} True if timezone is valid
* @returns {boolean} False if timezone is invalid
*/
function isTimezoneValid(timezone) {
const result = executeQuery(
`SELECT CONVERT_TIMEZONE(?, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP())`,
[timezone],
true
);
return !result.isErrored;
}
/**
* Generates a DMF type signature based on the arguments and entity columns
* @param {Array} dmfArguments - Array of DMF arguments
* @param {Object} entityColumnsMap - Map of entity names to column objects in the format { <ENTITY_NAME>: [ { name: <COLUMN_NAME> , dataType: <DATA_TYPE> } ] }
* @param {string} baseEntityName - Name of the base entity
* @returns {string} DMF type signature
* @throws {Error} If entity not found in the cache
*/
function generateDMFTypeSignature(
dmfArguments,
entityColumnsMap,
baseEntityName
) {
if (!dmfArguments || !dmfArguments.length) return "";
const baseEntityColumns = entityColumnsMap[baseEntityName];
if (!baseEntityColumns) {
throw new Error(`Entity ${baseEntityName} not found in the cache`);
}
const baseEntityColumnArguments = dmfArguments
.filter((param) => param.type === "COLUMN")
.map((param) => {
const column = baseEntityColumns.find((col) => col.name === param.name);
return column ? column.dataType : null;
})
.join(", ");
const baseEntityArguments = `TABLE(${baseEntityColumnArguments})`;
const referencedEntityArguments = dmfArguments
.filter((param) => param.type === "TABLE")
.map((entityParam) => {
const entityName = entityParam.name;
const entityColumns = entityColumnsMap[entityName];
if (!entityColumns) {
throw new Error(`Entity ${entityName} not found in the cache`);
}
const columnTypes = entityParam.nested
.map((nestedParam) => {
const column = entityColumns.find(
(col) => col.name === nestedParam.name
);
return column ? column.dataType : null;
})
.filter(Boolean)
.join(", ");
return `TABLE(${columnTypes})`;
});
const arguments = [baseEntityArguments, ...referencedEntityArguments].join(
", "
);
return arguments;
}
/**
* Generates DMF arguments for SQL statements
* @param {Array} dmfArguments - Array of DMF arguments
* @returns {string} Formatted DMF arguments for SQL statements
*/
function generateDMFColumnArguments(dmfArguments) {
return dmfArguments
.map((param) => {
if (param.type === "COLUMN") {
return normalizeIdentifier(param.name);
}
// Handle TABLE type with nested columns
return `TABLE(${param.name}(${param.nested
.map((nested) => normalizeIdentifier(nested.name))
.join(", ")}))`;
})
.join(", ");
}
/**
* Generates function parameters from DMF arguments
* @param {Array} dmfArguments - Array of DMF arguments
* @returns {string} Formatted function parameters
*/
function generateFunctionParameters(dmfArguments) {
return dmfArguments
.map((param) => {
if (param.type === "TABLE") {
const nestedParams = param.nested
.map((nested) => `${nested.name} ${nested.dataType}`)
.join(", ");
return `${param.name} TABLE(${nestedParams})`;
}
return `${param.name} ${param.dataType}`;
})
.join(", ");
}
// -----------------------------------------------------VALIDATION FUNCTIONS-----------------------------------------------------
/**
* Validates that mandatory arguments are provided and valid
* @throws {Error} If any mandatory argument is missing or invalid
*/
function validateMandatoryArguments() {
const VALID_ACTIONS = new Set([
"GET_PROCEDURE_VERSION", "ATTACH_DMF", "ATTACH_DMF_WITH_ROLE", "DETACH_DMF", "SUSPEND_DMF", "RESUME_DMF", "UPDATE_SCHEDULE", "CREATE_DMF", "EXECUTE_SQL",
]);
const VALID_ENTITY_TYPES = new Set([
"TABLE", "VIEW", "MATERIALIZED VIEW", "EXTERNAL TABLE", "ICEBERG TABLE",
]);
const DMF_OPS = new Set([
"ATTACH_DMF", "ATTACH_DMF_WITH_ROLE", "DETACH_DMF", "SUSPEND_DMF", "RESUME_DMF",
]);
const VALID_SCHEDULE_TYPES = new Set([
"MINUTES", "CRON", "ON_DATA_CHANGE", "NOT_SCHEDULED",
]);
const SCHEDULE_TYPES_THAT_REQUIRE_VALUE = new Set(["MINUTES", "CRON"]);
if (!VALID_ACTIONS.has(ACTION))
throw new Error(
`Invalid ACTION: "${ACTION}". Valid options are ${Array.from(
VALID_ACTIONS
).join(", ")}`
);
if (DMF_OPS.has(ACTION) || ACTION === "UPDATE_SCHEDULE") {
if (!ENTITY_TYPE) throw new Error("ENTITY_TYPE is required for DMF related actions");
}
if (ENTITY_TYPE && !VALID_ENTITY_TYPES.has(ENTITY_TYPE))
throw new Error(
`Invalid ENTITY_TYPE: "${ENTITY_TYPE}". Valid options are ${Array.from(
VALID_ENTITY_TYPES
).join(", ")}`
);
if (DMF_OPS.has(ACTION) && !DMF_NAME)
throw new Error("DMF_NAME is required for DMF related actions");
if (ACTION === "UPDATE_SCHEDULE") {
if (!SCHEDULE_TYPE)
throw new Error("SCHEDULE_TYPE is required for SCHEDULE action");
if (!VALID_SCHEDULE_TYPES.has(SCHEDULE_TYPE))
throw new Error(
`Invalid schedule type: "${SCHEDULE_TYPE}". Valid options are ${Array.from(
VALID_SCHEDULE_TYPES
).join(", ")}`
);
if (SCHEDULE_TYPES_THAT_REQUIRE_VALUE.has(SCHEDULE_TYPE) && !SCHEDULE_VALUE)
throw new Error("SCHEDULE_VALUE is required for SCHEDULE action");
}
if (ACTION === "EXECUTE_SQL" && !DMF_DEFINITION) {
throw new Error("Please provide a SQL query to execute.");
}
}
/**
* Validates the format of a fully qualified name (database.schema.name)
* @param {string} fullyQualifiedName - Name to validate
* @throws {Error} If invalid fully qualified name
*/
function validateFullyQualifiedName(fullyQualifiedName) {
const parts = fullyQualifiedName
.split(".")
.map((part) => part.trim())
.filter(Boolean);
if (parts.length !== 3)
throw new Error(
`Invalid fully qualified name: ${fullyQualifiedName}. Expected format: database.schema.name`
);
}
/**
* Validates the structure of DMF arguments JSON
* @param {string} rawDMFArguments - Raw JSON string of DMF arguments
* @throws {Error} If DMF arguments structure is invalid
*/
function validateDMFArgumentsStructure(rawDMFArguments) {
const parsedStructure = safelyParseJSON(rawDMFArguments);
if (!parsedStructure)
throw new Error("Invalid DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON. Expected a valid JSON string");
if (!Array.isArray(parsedStructure))
throw new Error("DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON must be an array");
const referencedEntities = parsedStructure.filter(
(param) => param.type === "TABLE"
);
if (referencedEntities.length > 1)
throw new Error("Only one referenced entity is allowed");
const validationFunctions = {
arrayItem: (param) =>
["COLUMN", "TABLE"].includes(param.type) && param.name,
nestedItem: (param) => ["COLUMN"].includes(param.type) && param.name,
};
if (!parsedStructure.every(validationFunctions.arrayItem))
throw new Error(
"Each parameter must have a valid type(TABLE/COLUMN) and name field"
);
if (referencedEntities.length > 0) {
for (const referencedEntity of referencedEntities) {
if (
!Array.isArray(referencedEntity.nested) ||
!referencedEntity.nested.every(validationFunctions.nestedItem)
)
throw new Error("Invalid nested parameters");
}
}
}
/**
* Validates that all specified columns exist in an entity
* @param {string} entityName - Name of the entity for error messages
* @param {Array} allColumnsInEntity - Column metadata from the entity
* @param {Array} columnsToCheck - Column names to validate
* @throws {Error} If any column doesn't exist in the entity
*/
function validateColumnsExistInEntity(
entityName,
allColumnsInEntity,
columnsToCheck
) {
for (const column of columnsToCheck) {
if (!allColumnsInEntity.some((col) => col.name === column))
throw new Error(`Column ${column} not found in entity ${entityName}`);
}
}
/**
* Validates that all provided identifiers exist and are accessible
* Checks entity names, column names, and DMF compatibility
* @param {string} entityName - Fully qualified name of the entity
* @param {string} dmfName - Fully qualified name of the DMF
* @param {Array} dmfArguments - Array of DMF arguments
* @throws {Error} If any identifier doesn't exist or is inaccessible
*/
function validateProvidedIdentifiers(
entityName,
dmfName = "",
dmfArguments = []
) {
if (!entityName) {
throw new Error(
"Please provide a valid entity name. The entity name is required to validate identifiers."
);
}
validateFullyQualifiedName(entityName);
// Validate the provided entity names and store all the columns for each entity in a map
const baseEntityName = entityName;
const baseEntityAllColumns = getAllColumnsForEntity(entityName);
const entityColumnsMap = { [baseEntityName]: baseEntityAllColumns };
const allReferencedEntities = dmfArguments.filter(
(param) => param.type === "TABLE"
);
for (const referencedEntity of allReferencedEntities) {
const columns = getAllColumnsForEntity(referencedEntity.name);
entityColumnsMap[referencedEntity.name] = columns;
}
// Validate all of the provided columns are valid and exist in their respective entities
const allBaseEntityColumnsInArguments = dmfArguments
.filter((param) => param.type === "COLUMN")
.map((param) => param.name);
validateColumnsExistInEntity(
baseEntityName,
baseEntityAllColumns,
allBaseEntityColumnsInArguments
);
for (const referencedEntity of allReferencedEntities) {
const columnsInArguments = referencedEntity.nested.map(
(nestedParam) => nestedParam.name
);
validateColumnsExistInEntity(
referencedEntity.name,
entityColumnsMap[referencedEntity.name],
columnsInArguments
);
}
if (dmfName) {
// Validate that the DMF is valid and exists
const generatedTypeSignature = generateDMFTypeSignature(
dmfArguments,
entityColumnsMap,
baseEntityName
);
isDMFValid(dmfName, generatedTypeSignature);
}
// All provided identifiers are valid, actually exist and are accessible to the procedure owner
}
/**
* Validates CRON expression syntax
* Performs detailed validation of all CRON components and timezones to protect against SQL injection
* @param {string} cronExpression - CRON expression to validate
* @throws {Error} If CRON expression is invalid
*/
function validateCronExpression(cronExpression) {
if (cronExpression.length > 100)
throw new Error("Cron expression is too long");
const cronFields = cronExpression.trim().split(/\s+/);
if (cronFields.length !== 6)
throw new Error("Invalid cron expression. Expected 6 fields");
const [minute, hour, dayOfMonth, month, dayOfWeek, timezone] = cronFields;
const isTimezoneValidResult = isTimezoneValid(timezone);
if (!isTimezoneValidResult)
throw new Error("Invalid timezone provided in the cron expression");
const regexPatterns = {
minute: /^(\*|\d+|\*\/\d+|\d+\-\d+|\d+(,\d+)*)$/,
hour: /^(\*|\d+|\*\/\d+|\d+\-\d+|\d+(,\d+)*)$/,
dayOfMonth: /^(\*|L|\d+|\*\/\d+|\d+\-\d+|\d+(,\d+)*)$/,
month:
/^(\*|\d+|JAN|FEB|MAR|APR|MAY|JUN|JUL|AUG|SEP|OCT|NOV|DEC|\*\/\d+|\d+\-\d+|[A-Z]{3}\-[A-Z]{3}|\d+(,\d+)*|([A-Z]{3}(,[A-Z]{3})*))$/i,
dayOfWeek:
/^(\*|\d+|SUN|MON|TUE|WED|THU|FRI|SAT|\d+L|[A-Z]{3}L|\*\/\d+|\d+\-\d+|[A-Z]{3}\-[A-Z]{3}|\d+(,\d+)*|([A-Z]{3}(,[A-Z]{3})*))$/i,
};
if (minute.match(/^\d+$/))
if (!isNumberValid(minute, 0, 59)) throw new Error("Invalid minute value");
if (hour.match(/^\d+$/))
if (!isNumberValid(hour, 0, 23)) throw new Error("Invalid hour value");
if (dayOfMonth.match(/^\d+$/))
if (!isNumberValid(dayOfMonth, 1, 31))
throw new Error("Invalid day of month value");
if (month.match(/^\d+$/))
if (!isNumberValid(month, 1, 12)) throw new Error("Invalid month value");
if (dayOfWeek.match(/^\d+$/))
if (!isNumberValid(dayOfWeek, 0, 6))
throw new Error("Invalid day of week value");
if (
!regexPatterns.minute.test(minute) ||
!regexPatterns.hour.test(hour) ||
!regexPatterns.dayOfMonth.test(dayOfMonth) ||
!regexPatterns.month.test(month) ||
!regexPatterns.dayOfWeek.test(dayOfWeek)
)
throw new Error("Invalid cron expression");
}
/**
* Validates schedule-specific arguments
* Ensures schedule type and value are compatible and valid
* @throws {Error} If schedule configuration is invalid
*/
function validateProvidedArgumentsForSchedule() {
const VALID_MINUTES = new Set(["5", "15", "30", "60", "720", "1440"]);
if (SCHEDULE_TYPE === "MINUTES" && !VALID_MINUTES.has(SCHEDULE_VALUE))
throw new Error(
`Invalid SCHEDULE_VALUE for MINUTES. Valid options are ${Array.from(
VALID_MINUTES
).join(", ")}`
);
if (SCHEDULE_TYPE === "CRON") validateCronExpression(SCHEDULE_VALUE);
// SCHEDULE_VALUE is valid for the provided SCHEDULE_TYPE
}
/**
* Validates DMF arguments with dataType checks
* @param {string} rawDMFArguments - Raw JSON string of DMF arguments
* @throws {Error} If DMF arguments structure is invalid or dataType is missing
*/
function validateDMFArgumentsWithDataType(rawDMFArguments) {
const parsedStructure = safelyParseJSON(rawDMFArguments);
if (!parsedStructure)
throw new Error("Invalid DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON. Expected a valid JSON string");
if (!Array.isArray(parsedStructure))
throw new Error("DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON must be an array");
const validationFunctions = {
arrayItem: (param) => {
if (!["COLUMN", "TABLE"].includes(param.type) || !param.name) {
return false;
}
if (param.type === "COLUMN" && !param.dataType) {
throw new Error(`Missing dataType for COLUMN parameter: ${param.name}`);
}
return true;
},
nestedItem: (param) => {
if (!["COLUMN"].includes(param.type) || !param.name) {
return false;
}
if (!param.dataType) {
throw new Error(
`Missing dataType for nested COLUMN parameter: ${param.name}`
);
}
return true;
},
};
if (!parsedStructure.every(validationFunctions.arrayItem))
throw new Error(
"Each parameter must have a valid type(TABLE/COLUMN) and name field"
);
const referencedEntities = parsedStructure.filter(
(param) => param.type === "TABLE"
);
for (const referencedEntity of referencedEntities) {
if (
!Array.isArray(referencedEntity.nested) ||
!referencedEntity.nested.every(validationFunctions.nestedItem)
)
throw new Error("Invalid nested parameters");
}
}
/**
* Validates DMF name format
* @param {string} dmfName - Fully qualified name of the DMF
* @throws {Error} If DMF name format is invalid
*/
function validateDmfName(dmfName) {
const parts = dmfName
.split(".")
.map((part) => part.trim())
.filter(Boolean);
if (parts.length !== 3) {
throw new Error(
`Invalid DMF_NAME: ${dmfName}. Expected format: database.schema.name`
);
}
}
/**
* Validates that the provided SQL is read-only and doesn't contain dangerous operations
* @param {string} sqlExpression - SQL to validate
* @returns {boolean} Whether the SQL is safe
* @throws {Error} If SQL contains potentially dangerous operations
*/
function validateSqlExpression(sqlExpression) {
if (!sqlExpression) {
throw new Error(
"Please provide a SQL query. The SQL expression cannot be empty."
);
}
// Step 1: Normalize Unicode characters to prevent encoding-based attacks
const normalizedSql = sqlExpression.normalize("NFKC");
// Step 2: Remove comments once up front
const sqlWithoutComments = removeSqlComments(normalizedSql);
// Step 3: Check for multiple statements
splitIntoSqlStatements(sqlWithoutComments);
// Step 4: Check whether it is a read-query or not
if (!isReadQuery(sqlWithoutComments)) {
throw new Error(
"Your query must start with SELECT or WITH. Only read operations are allowed."
);
}
// Step 5: Check for suspicious patterns that might bypass filters
checkForSuspiciousPatterns(sqlWithoutComments);
// Step 6: Check for dangerous operations
const dangerousOperation = containsDangerousOperation(sqlWithoutComments);
if (dangerousOperation) {
throw new Error(
"For security reasons, this operation is not permitted. Please use only read operations in your query."
);
}
return true;
}
/**
* Removes SQL line (--) and block (/* *\/) comments
* @param {string} sql - SQL text
* @returns {string} SQL without comments
*/
function removeSqlComments(sql) {
const withoutLineComments = sql.replace(/--.*$/gm, '');
const withoutComments = withoutLineComments.replace(/\/\*[\s\S]*?\*\//g, '');
return withoutComments;
}
/**
* Enhanced detection of suspicious SQL patterns
* @param {string} sql - SQL query to check
* @throws {Error} If suspicious patterns are detected
*/
function checkForSuspiciousPatterns(sql) {
// Create a copy where string literals are masked to prevent false positives
const sqlWithoutStrings = sql
.replace(/'[^']*'/g, "'STRING_LITERAL'")
.replace(/"[^"]*"/g, '"STRING_LITERAL"');
const suspiciousPatterns = [
// Common SQL injection techniques
{
pattern: /\bOR\s+[0-9]+\s*=\s*[0-9]+\b/i,
message: "Suspicious always-true condition detected",
},
// Alias abuse detection
{
pattern: /\bAS\s+['"`]?.*?(DELETE|INSERT|UPDATE|DROP|ALTER|EXEC)\b/i,
message: "Suspicious alias detected",
},
// Hex encoding and other obfuscation techniques
{
pattern: /0x[0-9a-f]{10,}/i,
message: "Suspicious hex encoding detected",
},
{
pattern: /CHAR\s*\(\s*\d+(\s*,\s*\d+)+\s*\)/i,
message: "Character code conversion functions are not allowed",
},
];
// Check for suspicious patterns outside of string literals
for (const { pattern, message } of suspiciousPatterns) {
if (pattern.test(sqlWithoutStrings)) {
throw new Error(message);
}
}
}
/**
* Splits SQL into separate statements based on semicolons not in quotes
* @param {string} sql - SQL query
* @returns {string} - SQL query without semicolons
*/
function splitIntoSqlStatements(sql) {
let inSingleQuote = false;
let inDoubleQuote = false;
for (let i = 0; i < sql.length; i++) {
const char = sql[i];
// Handle quotes
if (char === "'" && sql[i - 1] !== "\\") {
inSingleQuote = !inSingleQuote;
} else if (char === '"' && sql[i - 1] !== "\\") {
inDoubleQuote = !inDoubleQuote;
}
// If semicolon outside of quotes, throw error
if (char === ";" && !inSingleQuote && !inDoubleQuote) {
throw new Error(
"Do not use semicolons to break or end your SQL statement. Submit your query without any semicolons."
);
}
}
// If we get here, there were no semicolons outside quotes
return sql.trim();
}
/**
* Checks if the SQL is a read-only query
* @param {string} sql - SQL query string
* @returns {boolean} - True if it's a read-only query
*/
function isReadQuery(sql) {
const normalizedSql = sql.replace(/\s+/g, " ").toUpperCase().trim();
if (normalizedSql.startsWith("SELECT ")) {
return true;
}
if (normalizedSql.startsWith("WITH ")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Checks if SQL contains any dangerous operations - using single keywords with word boundaries
* @param {string} sql - SQL query string
* @returns {string|null} - The dangerous operation found or null if safe
*/
function containsDangerousOperation(sql) {
// Normalize whitespace and convert to uppercase for comparison
const normalizedSql = sql.replace(/\s+/g, " ").toUpperCase();
// Snowflake-specific dangerous commands - using single keywords with high precision
const dangerousCommands = [
// Data Modification
"INSERT", "UPDATE", "DELETE", "MERGE", "TRUNCATE", "COPY",
// DDL statements
"CREATE", "DROP", "ALTER", "COMMENT", "GRANT", "REVOKE", "UNDROP",
// Transaction control
"BEGIN", "COMMIT", "ROLLBACK",
// System & session commands
"SET", "UNSET", "USE", "PUT", "GET", "REMOVE", "LIST",
// Information Schema & Metadata
"SHOW", "DESCRIBE",
// Procedures and functions
"CALL", "EXECUTE", "EXEC",
// Additional Snowflake operations
"EXPLAIN",
];
// Dangerous functions specific to Snowflake
const dangerousFunctions = [
"SYSTEM", "CURRENT_USER", "CURRENT_ROLE", "CURRENT_ACCOUNT", "DATABASE", "VERSION", "SLEEP", "CALL_INTEGRATION", "PARSE_JSON", "RUN_JAVASCRIPT", "CALL_JAVASCRIPT", "TO_JAVASCRIPT",
];
// Create a regex pattern with word boundaries for all dangerous commands
const commandPattern = new RegExp(
`\\b(${dangerousCommands.join("|")})\\b`,
"i"
);
const functionPattern = new RegExp(
`\\b(${dangerousFunctions.join("|")})\\s*\\(`,
"i"
);
// Check for dangerous commands
const commandMatch = normalizedSql.match(commandPattern);
if (commandMatch) {
return `Dangerous operation detected: ${commandMatch[0]}`;
}
// Check for dangerous functions
const functionMatch = normalizedSql.match(functionPattern);
if (functionMatch) {
return `Dangerous function call detected: ${functionMatch[1]}`;
}
// Check for access to sensitive metadata
if (/\bINFORMATION_SCHEMA\b|\bACCOUNT_USAGE\b/i.test(normalizedSql)) {
return "Access to sensitive system metadata detected";
}
return null;
}
/**
* Executes SQL and returns a numeric result
* @param {string} sql - SQL to execute
* @returns {number} Numeric result
* @throws {Error} If execution fails or result is not numeric
*/
function executeSqlAndReturnNumber(sql) {
try {
// Execute without returnFirstRow to get full result set
const result = executeQuery(sql, [], false);
if (result.isErrored) {
throw new Error(result.message);
}
// Check if the result set exists
if (!result.result) {
throw new Error(
"Your query didn't return any results. Please check your SQL and try again."
);
}
// Check number of columns
const columnCount = result.result.getColumnCount();
if (columnCount !== 1) {
throw new Error(
"Your query should return exactly one column. Please modify your query to return a single numeric value."
);
}
// Check if we have exactly one row
if (!result.result.next()) {
throw new Error(
"Your query didn't return any rows. Please check your query and try again."
);
}
// Get the value
const value = result.result.getColumnValue(1);
// Check if it's a number
if (typeof value !== "number") {
throw new Error(
"Your query must return a number. Please modify your query to calculate a numeric result."
);
}
// Check if there are more rows
if (result.result.next()) {
throw new Error(
"Your query returned multiple rows. Please modify your query to return a single result."
);
}
return value;
} catch (err) {
throw new Error(`${err.message}`);
}
}
/**
* Validates all parameters for DMF creation
* @throws {Error} If any validation fails
*/
function validateCreateDmf() {
validateDmfName(DMF_NAME);
validateSqlExpression(DMF_DEFINITION);
validateDMFArgumentsWithDataType(DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON);
}
/**
* Validates all provided arguments
* Performs comprehensive validation on input parameters
* @throws {Error} If any validation fails
*/
function validateAllArguments() {
validateMandatoryArguments(); // Validates all mandatory arguments are provided in the correct format
if (ACTION === "GET_PROCEDURE_VERSION") {
return;
}
if (ACTION === "CREATE_DMF") {
validateCreateDmf();
return;
} else if (ACTION === "EXECUTE_SQL") {
validateSqlExpression(DMF_DEFINITION);
return;
}
else {
if (ACTION === "UPDATE_SCHEDULE") {
validateProvidedArgumentsForSchedule(); // Validates the provided schedule type and value
} else {
validateDMFArgumentsStructure(DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON);
}
validateProvidedIdentifiers(
ENTITY_NAME,
DMF_NAME,
safelyParseJSON(DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON)
); // All provided arguments are valid and legal
}
}
// -----------------------------------------------------MAIN FUNCTION-----------------------------------------------------
/**
* Extracts database, schema and table name from fully qualified entity name
* @param {string} entityName - Fully qualified entity name
* @returns {Object} Object containing database, schema and table name
*/
function parseEntityName(entityName) {
const [db, schema, table] = entityName.split(".");
return { db, schema, table };
}
/**
* Gets the owner of a table from information schema
* @param {string} db - Database name
* @param {string} schema - Schema name
* @param {string} table - Table name
* @returns {Object} Object containing success status and table owner
*/
function getTableOwner(db, schema, table) {
const query = `SELECT TABLE_OWNER FROM ${db}.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_CATALOG = ? AND TABLE_SCHEMA = ? AND TABLE_NAME = ?`;
const result = executeQuery(query, [db, schema, table], true);
if (result.isErrored) {
return {
isSuccessful: false,
message: `Failed to get table owner: ${result.message}`,
owner: null,
};
}
const owner = result.result?.getColumnValue("TABLE_OWNER");
if (!owner) {
return {
isSuccessful: false,
message: `Could not find owner for table ${db}.${schema}.${table}`,
owner: null,
};
}
return {
isSuccessful: true,
message: "Successfully retrieved table owner",
owner,
};
}
/**
* Grants required permissions to a role
* @param {string} currentDatabase - Current database name
* @param {string} role - Role to grant permissions to
* @returns {Object} Object containing success status and message
*/
function grantPermissions(currentDatabase, role) {
const dbIdent = normalizeIdentifier(currentDatabase);
const query = `
BEGIN
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA ${dbIdent}.DMFS TO ROLE "${role}";
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE ${dbIdent} TO ROLE "${role}";
GRANT USAGE ON ALL FUNCTIONS IN SCHEMA ${dbIdent}.DMFS TO ROLE "${role}";
END;
`;
const result = executeQuery(query, []);
if (result.isErrored) {
return {
isSuccessful: false,
message: `Failed to grant permissions: ${result.message}`,
};
}
return {
isSuccessful: true,
message: `Successfully granted permissions to role ${role}`,
};
}
/**
* Handles permissions for DMF operations
* @param {string} currentDatabase - Current database name
* @param {string} entityName - Fully qualified entity name
* @returns {Object} Object containing success status and message
*/
function handleDMFPermissions(currentDatabase, entityName) {
try {
// Parse entity name
const { db, schema, table } = parseEntityName(entityName);
// Get table owner
const ownerResult = getTableOwner(db, schema, table);
if (!ownerResult.isSuccessful) {
return ownerResult;
}
// Grant permissions
return grantPermissions(currentDatabase, ownerResult.owner);
} catch (err) {
return {
isSuccessful: false,
message: `Error handling permissions: ${err.message}`,
};
}
}
/**
* Executes DMF attach/detach/suspend/resume operations
* @param {string} action - One of ATTACH_DMF, ATTACH_DMF_WITH_ROLE, DETACH_DMF, SUSPEND_DMF, RESUME_DMF
*/
function modifyDMFAttachment(action) {
const currentDatabase = getCurrentDatabaseName();
const dqAdminRoleName = getDatabaseOwnerRole(currentDatabase);
const permissionResult = handleDMFPermissions(currentDatabase, ENTITY_NAME);
if (!permissionResult.isSuccessful) {
return JSON.stringify(permissionResult);
}
const dmfArguments = generateDMFColumnArguments(
safelyParseJSON(DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON)
);
const SQL_TEMPLATES = {
ATTACH_DMF: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} ADD DATA METRIC FUNCTION ${DMF_NAME} ON (${dmfArguments})`,
ATTACH_DMF_WITH_ROLE: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} ADD DATA METRIC FUNCTION ${DMF_NAME} ON (${dmfArguments}) EXECUTE AS ROLE "${dqAdminRoleName}"`,
DETACH_DMF: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} DROP DATA METRIC FUNCTION ${DMF_NAME} ON (${dmfArguments})`,
SUSPEND_DMF: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} MODIFY DATA METRIC FUNCTION ${DMF_NAME} ON (${dmfArguments}) SUSPEND`,
RESUME_DMF: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} MODIFY DATA METRIC FUNCTION ${DMF_NAME} ON (${dmfArguments}) RESUME`,
};
const sqlText = SQL_TEMPLATES[action];
const result = executeQuery(sqlText, []);
if (result.isErrored) {
return JSON.stringify({
isSuccessful: false,
message: result.message,
});
}
return JSON.stringify({
isSuccessful: !result.isErrored,
message: result.isErrored
? result.message
: `ACTION: ${action} performed successfully on ${ENTITY_NAME} with DMF: ${DMF_NAME} and DMF Arguments: ${dmfArguments}`,
});
}
/**
* Checks if a role exists
* @param {string} roleName - Role to check
* @returns {boolean} True if role exists
*/
function doesRoleExist(roleName) {
const query = `SHOW GRANTS ON ROLE IDENTIFIER(?)`;
const res = executeQuery(query, [roleName], true);
return !res.isErrored;
}
/**
* Updates schedule on an entity
*/
function updateSchedule() {
const SQL_TEMPLATES = {
MINUTES: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} SET DATA_METRIC_SCHEDULE = '${SCHEDULE_VALUE} MINUTE'`,
CRON: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} SET DATA_METRIC_SCHEDULE = 'USING CRON ${SCHEDULE_VALUE}'`,
ON_DATA_CHANGE: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} SET DATA_METRIC_SCHEDULE = 'TRIGGER_ON_CHANGES'`,
NOT_SCHEDULED: `ALTER ${ENTITY_TYPE} ${ENTITY_NAME} UNSET DATA_METRIC_SCHEDULE`,
};
const sqlText = SQL_TEMPLATES[SCHEDULE_TYPE];
const result = executeQuery(sqlText, []);
return JSON.stringify({
isSuccessful: !result.isErrored,
message: result.isErrored
? result.message
: `Successfully updated schedule for ${ENTITY_NAME} to ${SCHEDULE_TYPE} ${SCHEDULE_VALUE}`,
});
}
/**
* Creates a DMF with dynamic return type fallback
*/
function createDmf(returnType = "NUMBER") {
const DOLLAR = String.fromCharCode(36);
const dmfArguments = safelyParseJSON(DMF_ARGUMENTS_JSON);
const functionParams = generateFunctionParameters(dmfArguments);
const sqlText = `CREATE OR REPLACE DATA METRIC FUNCTION ${DMF_NAME} (${functionParams})\nRETURNS\n${returnType}\nAS\n${DOLLAR}${DOLLAR}\n${DMF_DEFINITION}\n${DOLLAR}${DOLLAR};`;
const result = executeQuery(sqlText);
if (
result.isErrored &&
result.message.includes("incompatible with actual return type") &&
result.message.includes("FLOAT")
) {
return createDmf("FLOAT");
}
const returnMessage = `DMF ${DMF_NAME} registered successfully`;
return JSON.stringify({
isSuccessful: !result.isErrored,
message: result.isErrored ? result.message : returnMessage,
});
}
/**
* Executes a read-only SQL and returns numeric result
*/
function executeSql() {
const result = executeSqlAndReturnNumber(DMF_DEFINITION);
return JSON.stringify({
isSuccessful: true,
message: "SQL executed successfully",
result: result,
});
}
function getProcedureVersion() {
return JSON.stringify({
isSuccessful: true,
message: "Procedure version retrieved successfully",
result: PROCEDURE_VERSION,
});
}
/**
* Main function to manage DMF operations
* Validates all arguments and executes the main logic
* @returns {string} JSON string with operation status and result message
* @throws {Error} If any operation step fails
*/
function main() {
validateAllArguments();
switch (ACTION) {
case "GET_PROCEDURE_VERSION":
return getProcedureVersion();
case "ATTACH_DMF":
case "DETACH_DMF":
case "SUSPEND_DMF":
case "RESUME_DMF":
case "ATTACH_DMF_WITH_ROLE":
return modifyDMFAttachment(ACTION);
case "UPDATE_SCHEDULE":
return updateSchedule();
case "CREATE_DMF":
return createDmf();
case "EXECUTE_SQL":
return executeSql();
default: {
throw new Error(
`Invalid ACTION: "${ACTION}".`
);
}
}
}
// Execute the main function and return the result
try {
return main();
} catch (err) {
return JSON.stringify({
isSuccessful: false,
message: err.message,
});
}
$$; -
Transfer ownership to
dq_adminrole:GRANT OWNERSHIP ON DATABASE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT OWNERSHIP ON SCHEMA IDENTIFIER($_SHARED_SCHEMA) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT OWNERSHIP ON SCHEMA IDENTIFIER($_DMFS_SCHEMA) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT OWNERSHIP ON PROCEDURE IDENTIFIER($_MANAGE_DMF_PROCEDURE)(
STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING
) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
Grant privileges
Grant the necessary permissions to enable data quality operations and maintain proper access control.
The permission model for data quality has been simplified. The DQ_ADMIN role now requires only SELECT access on your tables instead of table owner role grants. This change reduces privilege requirements while maintaining full functionality through Snowflake's EXECUTE AS ROLE feature. Existing setups with table owner role grants continue to work.
-
System privileges: Grant Snowflake system-level permissions to enable data metric functions and monitoring capabilities.
-- For DQ Admin Role
GRANT DATABASE ROLE SNOWFLAKE.DATA_METRIC_USER TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
-- For Atlan Service Role
GRANT APPLICATION ROLE SNOWFLAKE.DATA_QUALITY_MONITORING_VIEWER TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT DATABASE ROLE SNOWFLAKE.DATA_METRIC_USER TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT EXECUTE TASK ON ACCOUNT TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT EXECUTE MANAGED TASK ON ACCOUNT TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE); -
Database access: Grant Atlan's service role access to the created objects:
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA IDENTIFIER($_SHARED_SCHEMA) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA IDENTIFIER($_DMFS_SCHEMA) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT USAGE ON FUTURE FUNCTIONS IN SCHEMA IDENTIFIER($_DMFS_SCHEMA) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT USAGE ON PROCEDURE IDENTIFIER($_MANAGE_DMF_PROCEDURE)(
STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING, STRING
) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT CREATE SCHEMA ON DATABASE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_DATABASE) TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE); -
Data access for DQ_ADMIN: Grant SELECT access on your customer databases to enable data quality monitoring. Replace
<database-name>with your database names:-- Grant database and schema access
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT USAGE ON ALL SCHEMAS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
-- Grant SELECT on tables and views
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT SELECT ON ALL VIEWS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
-- Set up future grants for new objects
GRANT USAGE ON FUTURE SCHEMAS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT SELECT ON FUTURE TABLES IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT SELECT ON FUTURE VIEWS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
-- Grant Snowflake system privileges
GRANT DATABASE ROLE SNOWFLAKE.DATA_METRIC_USER TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE);
GRANT EXECUTE DATA METRIC FUNCTION ON ACCOUNT TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($DQ_ADMIN_ROLE); -
Reference access to tables and views: Grant access to the service role to reference objects. This doesn't grants access to the actual data inside the objects.
-
Database and schema usage: Enables Atlan to discover and reference objects.
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT USAGE ON ALL SCHEMAS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);- Replace
<database-name>and<schema-name>with your own object names.
- Replace
-
Table and view reference access: Required to attach and execute rules on these objects.
GRANT REFERENCES ON ALL TABLES IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT REFERENCES ON ALL VIEWS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);- Replace
<database-name>and<schema-name>with your own object names.
- Replace
-
Dynamic table monitoring (if you use Dynamic Tables):
GRANT MONITOR ON ALL DYNAMIC TABLES IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);- Replace
<database-name>with your own object name.
- Replace
-
Set up future grants to retain grants when objects are recreated and apply them to new objects automatically. If you define future grants at both database and schema levels, schema-level grants take precedence. For more information, see the Snowflake documentation about considerations for future grants.
GRANT USAGE ON FUTURE SCHEMAS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT REFERENCES ON FUTURE TABLES IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT REFERENCES ON FUTURE VIEWS IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT MONITOR ON FUTURE DYNAMIC TABLES IN DATABASE <database-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);- Replace
<database-name>and<schema-name>with your own object names.
If you use schema-level future grants, grant the following to the service role:
GRANT REFERENCES ON FUTURE TABLES IN SCHEMA <database-name>.<schema-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT REFERENCES ON FUTURE VIEWS IN SCHEMA <database-name>.<schema-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);
GRANT MONITOR ON FUTURE DYNAMIC TABLES IN SCHEMA <database-name>.<schema-name> TO ROLE IDENTIFIER($ATLAN_DQ_SERVICE_ROLE);- Replace
<database-name>and<schema-name>with your own object names.
- Replace
-
Next steps
- Enable data quality on connection - Configure your Snowflake connection for data quality monitoring
Need help
If you have questions or need assistance with setting up Snowflake for data quality, reach out to Atlan Support by submitting a support request.
See also
- Data quality permissions - Understand the required permissions and roles for data quality operations
- Configure alerts for data quality rules - Set up real-time notifications for rule failures